Mumps
Understanding Mumps: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Introduction
Mumps is a viral infection primarily affecting the salivary glands, particularly the parotid glands, which are located near the ears. It is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets or direct contact with an infected person. While it is now less common due to vaccination, outbreaks still occur, particularly in areas with low vaccination rates.
Causes of Mumps
- Mumps Virus (Paramyxovirus):The mumps virus is the sole cause of the infection. It spreads through:
- Saliva and Respiratory Droplets: When an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, the virus can spread to others.
- Direct Contact: Sharing utensils, cups, or close contact with someone who has mumps can lead to infection.
Symptoms of Mumps
Symptoms typically appear 2-3 weeks after exposure to the virus and may include:
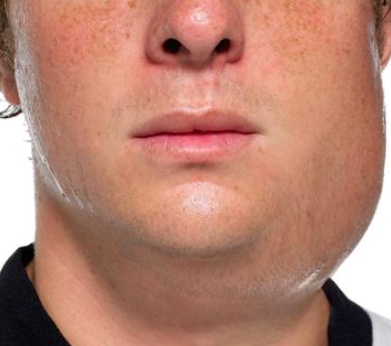
- Swollen, Painful Salivary Glands (Parotitis): This is the hallmark symptom, causing swelling on one or both sides of the face.
- Fever: Often mild but can reach up to 104°F (40°C).
- Headache: Generalized head pain is common.
- Muscle Aches: Especially in the neck and jaw area.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness and weakness.
- Loss of Appetite: A decreased desire to eat due to discomfort.
Complications (Rare but Serious)
- Orchitis: Inflammation of the testicles in males, which can lead to fertility issues.
- Oophoritis or Mastitis: Inflammation of the ovaries or breasts in females.
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes.
- Encephalitis: Brain inflammation, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Hearing Loss: Though rare, mumps can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Mumps
- Rest: Getting plenty of rest can help the body fight the infection.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially with fever.
- Soft Foods: To ease the pain of swollen glands, stick to soft foods like soups and smoothies.
- Warm or Cold Compresses: Applying compresses to the swollen glands can provide relief.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and fever.
Clinical Treatments for Mumps
- No Specific Antiviral Treatment: Mumps is a viral infection, so antibiotics are ineffective. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms until the infection clears on its own.
- Vaccination (MMR Vaccine): The best prevention against mumps is the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine. It is usually administered in childhood but can also be given to adults who haven’t been vaccinated or exposed.
- Isolation: To prevent the spread of mumps, people with the infection should avoid public places and isolate themselves for at least 5 days after the onset of symptoms.
Alternative/Non-Invasive Treatments for Mumps
For mumps, the therapies offered by Earl Claytont Wellness Centre may not directly treat the viral infection, but some treatments could support the body’s healing and alleviate symptoms:
- NAD+ Therapy:
- NAD+ therapy boosts the immune system, supports cellular repair, and reduces inflammation, which may help the body recover more effectively from viral infections like mumps. While it won't treat the virus itself, it can support overall immune function and recovery.
- Vitamin B Complex:
- B vitamins are crucial for immune function and energy production. Supplementing with a B Complex can help support the body’s natural defense mechanisms during viral infections like mumps, potentially aiding recovery and reducing fatigue.
- PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy):
- PEMF therapy may help reduce inflammation and support the body’s healing process, providing relief from symptoms like swelling and discomfort associated with mumps.
These therapies can help support the immune system, reduce inflammation, and promote recovery, but mumps generally require rest and time to resolve. It's important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Discover the perfect treatment for you with a FREE MEDICAL ASSESSMENT! Limited slots available – secure yours now by scheduling an appointment. Click below to book now!
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Severe Swelling or Pain: If swelling becomes severe or involves the testicles, abdomen, or breasts, medical attention is needed.
- High Fever or Neurological Symptoms: A high fever, stiff neck, or confusion may indicate complications like meningitis or encephalitis.
- Hearing Loss: Any signs of hearing difficulties should be evaluated by a doctor.
Conclusion
Mumps is a contagious viral infection that can cause painful swelling of the salivary glands and other complications. Though largely preventable through vaccination, managing symptoms and isolating affected individuals are key to preventing the spread and ensuring recovery.

