Sleep Apnea
Understanding Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Introduction
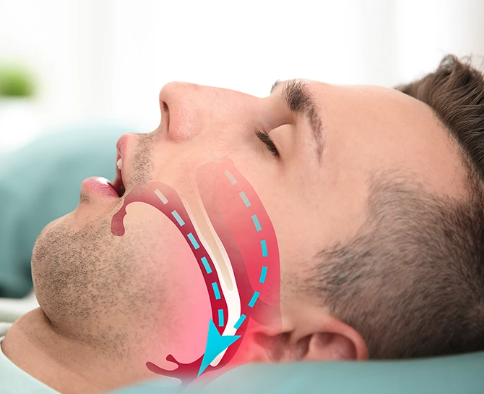
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder in which a person’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This disruption can lead to poor sleep quality and a range of health problems if left untreated. The two main types of sleep apnea are Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), the more common form, and Central Sleep Apnea (CSA), which occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA):
- Excess Weight: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor, as fat deposits around the upper airway can obstruct breathing.
- Narrow Airway: Some people inherit a naturally narrow throat or enlarged tonsils or adenoids, which can block the airway.
- Nasal Congestion: Chronic congestion or structural problems in the nasal passages can contribute to OSA.
- Age and Gender: Men and older adults are more likely to develop OSA.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA):
- Brain Function Issues: CSA occurs when the brain doesn’t send signals to the breathing muscles, often due to heart failure, stroke, or certain medications that affect the central nervous system.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
- Loud Snoring: Common in OSA, though not everyone with sleep apnea snores.
- Gasping or Choking During Sleep: Breathing interruptions may cause choking, snorting, or gasping.
- Daytime Sleepiness: Poor sleep quality leads to excessive daytime sleepiness or fatigue.
- Morning Headaches: Frequent headaches upon waking.
- Dry Mouth or Sore Throat: Waking up with a dry mouth is common, especially in OSA.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Cognitive issues such as forgetfulness, irritability, or trouble focusing.
- Mood Changes: Depression, irritability, or mood swings may occur.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss:
- Losing even a small amount of weight can help reduce airway obstruction in OSA.
- Positional Therapy:
- Sleeping on your side instead of your back can reduce the likelihood of airway blockages during sleep.
- Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives:
- These substances relax the muscles in the throat, increasing the risk of airway collapse.
- Humidifiers:
- Adding moisture to the air can help reduce nasal congestion and make breathing easier during sleep.
- Regular Exercise:
- Exercise improves overall health and may help reduce sleep apnea symptoms, even if it doesn’t lead to weight loss.
Clinical Treatments for Sleep Apnea
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP):
- The most common and effective treatment for OSA, CPAP uses a machine that delivers steady air pressure through a mask to keep the airway open during sleep.
- Oral Appliances:
- Dental devices designed to keep the throat open by repositioning the jaw or tongue are available for mild to moderate OSA.
- Surgery:
- Surgical options may be considered for those with anatomical problems, such as enlarged tonsils or a deviated septum. Surgeries include:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removes tissue from the back of the throat to widen the airway.
- Genioglossus Advancement: Repositions the tongue to prevent airway blockage.
- Surgical options may be considered for those with anatomical problems, such as enlarged tonsils or a deviated septum. Surgeries include:
- Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV):
- A device used primarily for CSA, it adjusts pressure based on the patient’s breathing patterns and helps maintain regular breathing during sleep.
- Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP):
- Similar to CPAP, BiPAP provides two levels of pressure: one for inhalation and another for exhalation, and is used for people who can’t tolerate CPAP.
Alternative/Non-Invasive Treatments for Sleep Apnea
For sleep apnea, the therapies offered by Earl Claytont Wellness Centre that may support overall health and help manage symptoms include:
- PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy):
PEMF therapy can improve circulation and reduce inflammation, which may benefit individuals with sleep apnea by promoting better oxygen flow and reducing airway obstruction. It may also help improve sleep quality by relaxing muscles and reducing tension in the upper airway. - NAD+ Therapy:
NAD+ therapy supports cellular repair, energy production, and mitochondrial function. This may help improve overall health and reduce oxidative stress, which could indirectly benefit sleep apnea patients by improving respiratory health and reducing fatigue during the day. - Full Spectrum Infrared Sauna:
Infrared sauna therapy promotes detoxification and relaxation, potentially helping with weight loss and improving respiratory health, both of which can play a role in managing obstructive sleep apnea. - Vitamin B Complex:
B vitamins, particularly B6 and B12, are essential for maintaining healthy nerve and muscle function. A B Complex supplement may support respiratory health and improve energy levels, which can be beneficial for those experiencing fatigue and disrupted sleep due to sleep apnea.
These therapies can help improve overall health, reduce inflammation, and support better respiratory function, but sleep apnea usually requires specific treatments like CPAP machines or medical interventions to directly address the airway obstruction.
Discover the perfect treatment for you with a FREE MEDICAL ASSESSMENT! Limited slots available – secure yours now by scheduling an appointment. Click below to book now!
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Persistent Symptoms: If you experience loud snoring, frequent pauses in breathing, or excessive daytime fatigue, consult a doctor for evaluation.
- Cardiovascular Symptoms: People with sleep apnea are at higher risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke, so treatment is essential.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder that can lead to significant health issues if untreated. With proper diagnosis and treatment, including lifestyle changes, CPAP therapy, or surgical intervention, individuals with sleep apnea can achieve better sleep quality and improved overall health. If you suspect you have sleep apnea, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and management.

